# RBAC权限模型(Role-Based Access Control)
前面主要介绍了元数据管理和业务数据的处理,通常一个系统都会有多个用户,不同用户具有不同的权限,本文主要介绍基于RBAC动态权限管理在crudapi中的实现。
# 概要
# RBAC简介
RBAC权限模型(Role-Based Access Control)即:基于角色的权限控制。模型中有几个关键的术语:
用户:系统接口及访问的操作者
权限:能够访问某接口或者做某操作的授权资格
角色:具有一类相同操作权限的用户的总称
# 用户角色权限关系
一个用户有一个或多个角色
一个角色包含多个用户
一个角色有多种权限
一个权限属于多个角色
# Spring security
Spring Security是Spring项目组中用来提供安全认证服务的框架,可以很方便的实现动态权限管理。
# 表单配置
系统内置5个表单,这些表单和权限相关,和具体业务无关
# 资源resource
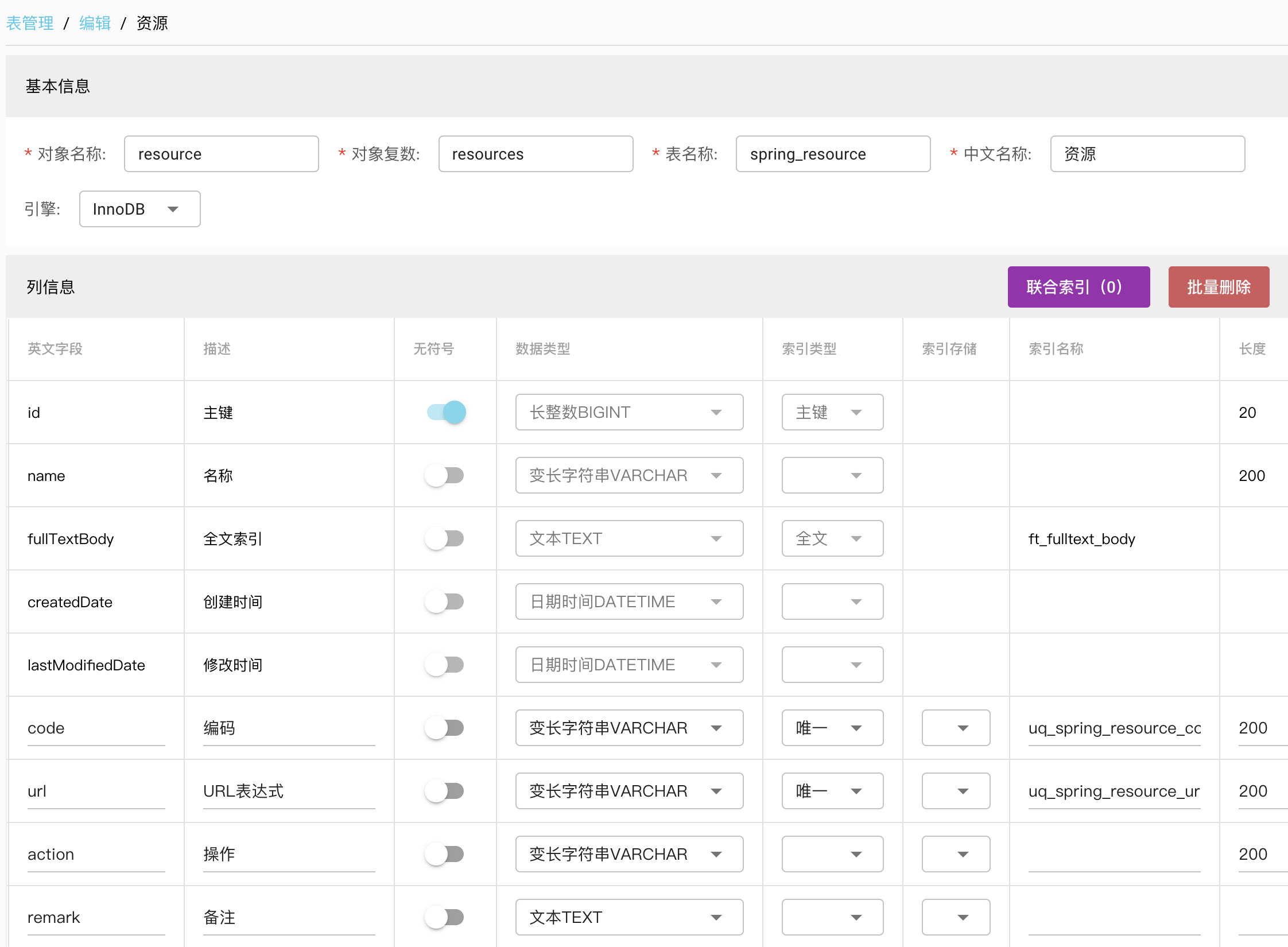 其中url是ANT格式表达式,用于配置url来确定是否拥有某个资源的权限。
其中url是ANT格式表达式,用于配置url来确定是否拥有某个资源的权限。
# 用户user
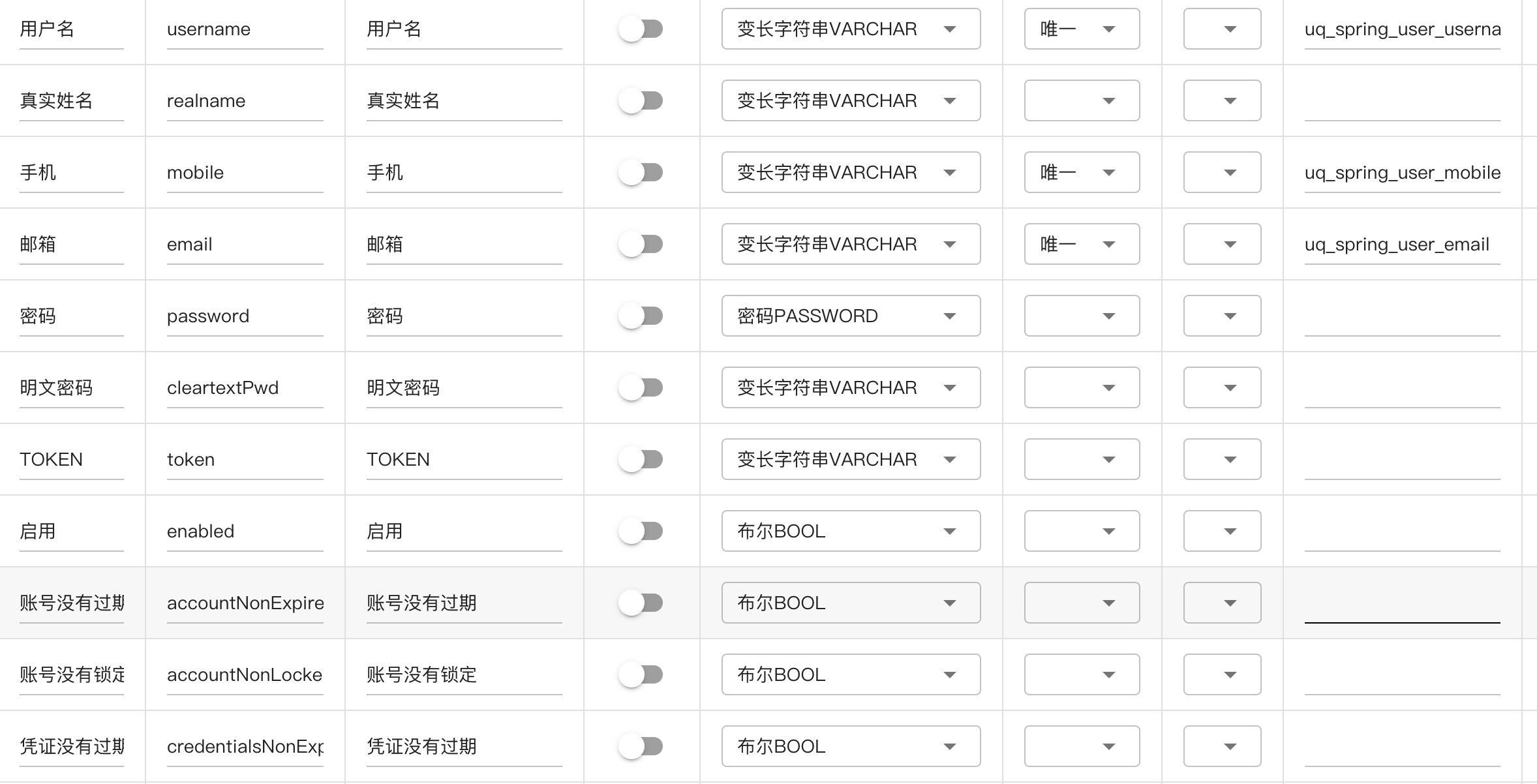 用户表记录登录用户信息
用户表记录登录用户信息
# 角色role
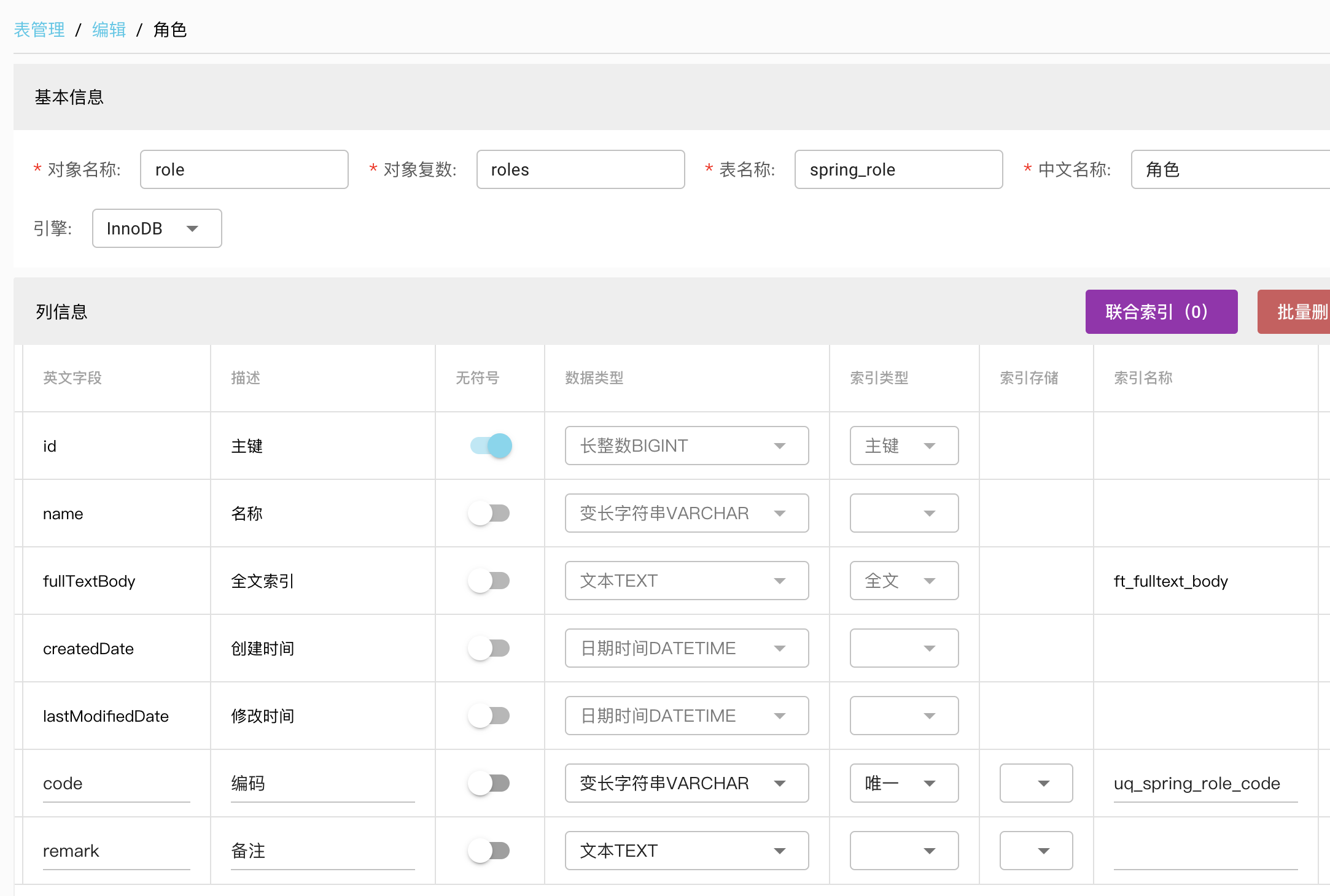 角色
角色
# 用户角色行userRoleLine
 用户和角色的中间表,参考之前表关系管理,利用两个一对多建立多对多关系,
用户和角色的中间表,参考之前表关系管理,利用两个一对多建立多对多关系,
# 角色资源行roleResourceLine
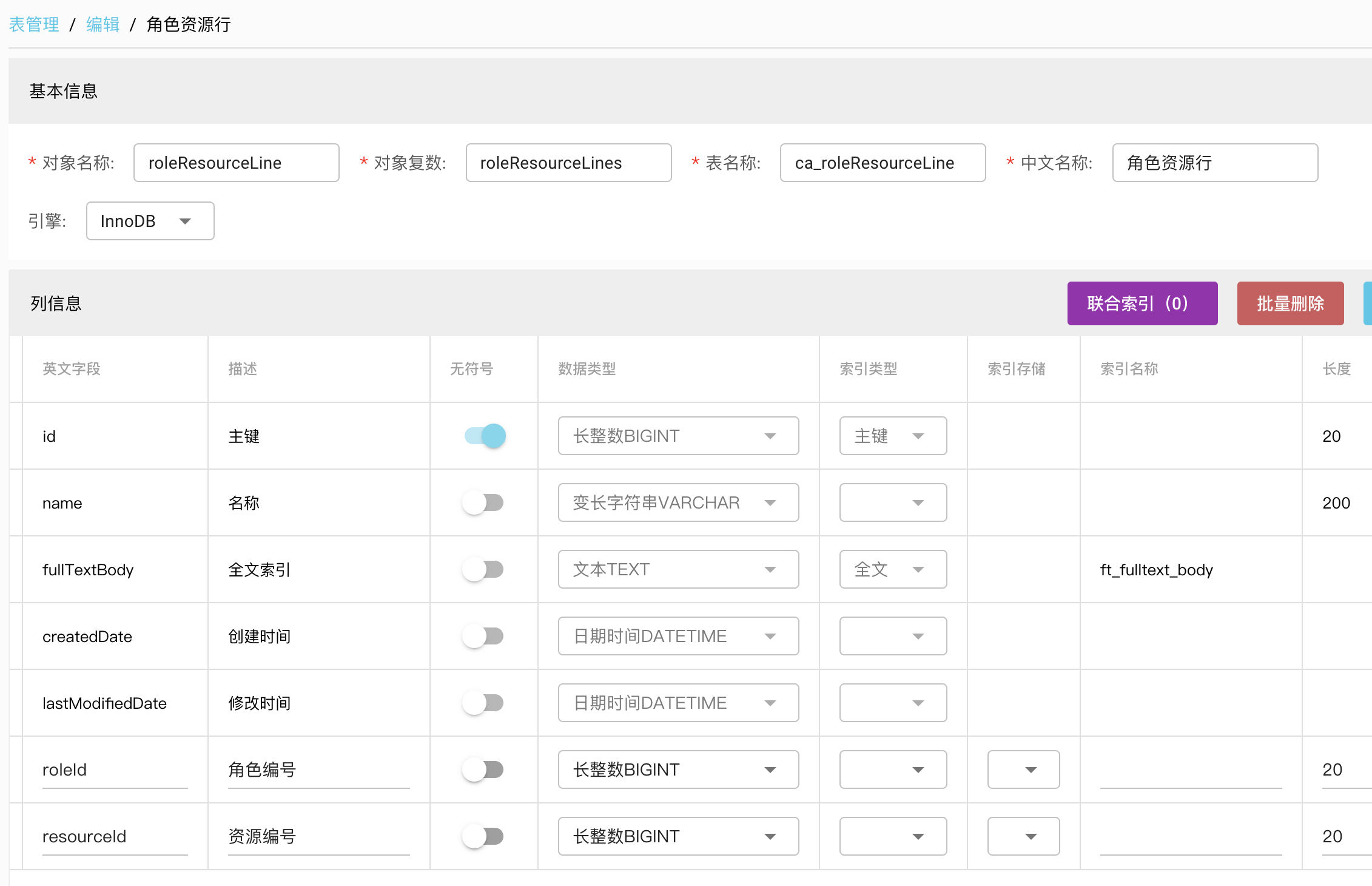 角色和资源的中间表,同样的利用两个一对多建立多对多关系
角色和资源的中间表,同样的利用两个一对多建立多对多关系
# 表关系
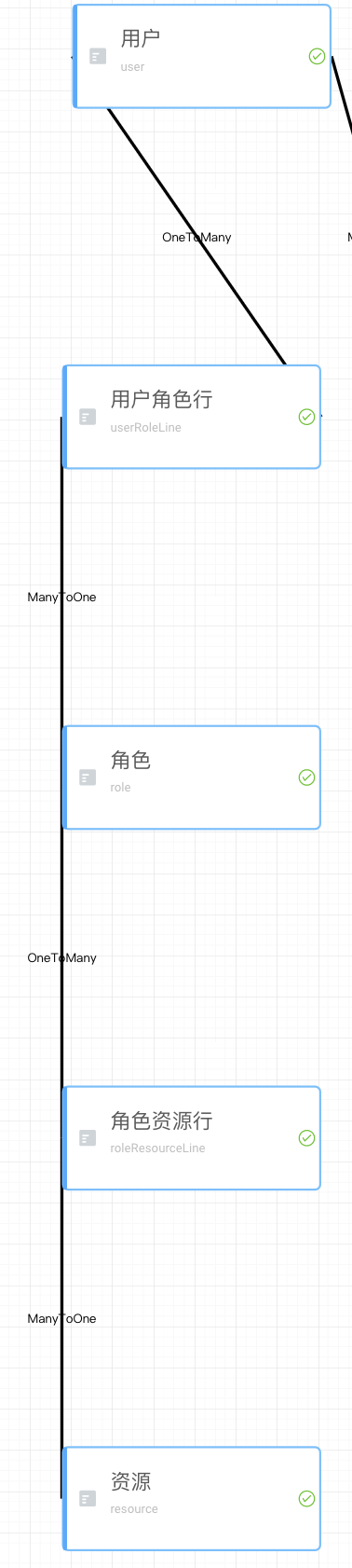
| 原表 | 目标表 | 关系 |
|---|---|---|
| user | userRoleLine | 一对多 |
| userRoleLine | role | 多对一 |
| role | roleResourceLine | 一对多 |
| roleResourceLine | resource | 多对一 |
# 权限控制原理
根据登录用户首选获取角色列表,每个角色对应多个资源,最终用户的权限为多个角色对应的资源叠加。如果拥有某个资源权限就返回数据,否则提示无权限。
默认如果没有匹配任何资源,表示该资源无需特别权限,只需要登录用户即可。
# 验证
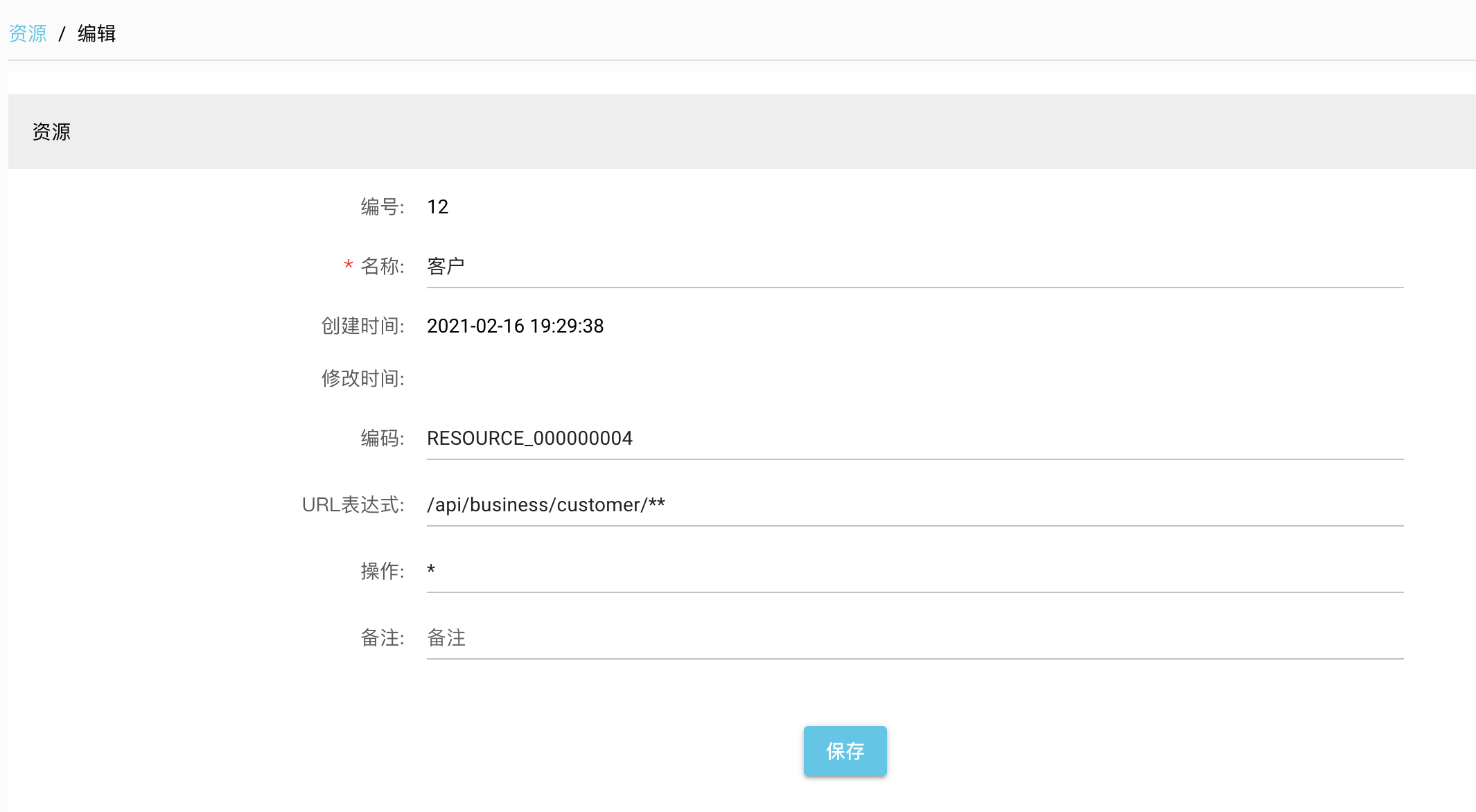 添加客户资源,ANT url为/api/business/customer/**,操作为*,表示GET,PATCH,DELETE,POST都需要授权。
如果操作为DELETE,表示值控制DELETE操作,其它操作不限制。
添加客户资源,ANT url为/api/business/customer/**,操作为*,表示GET,PATCH,DELETE,POST都需要授权。
如果操作为DELETE,表示值控制DELETE操作,其它操作不限制。
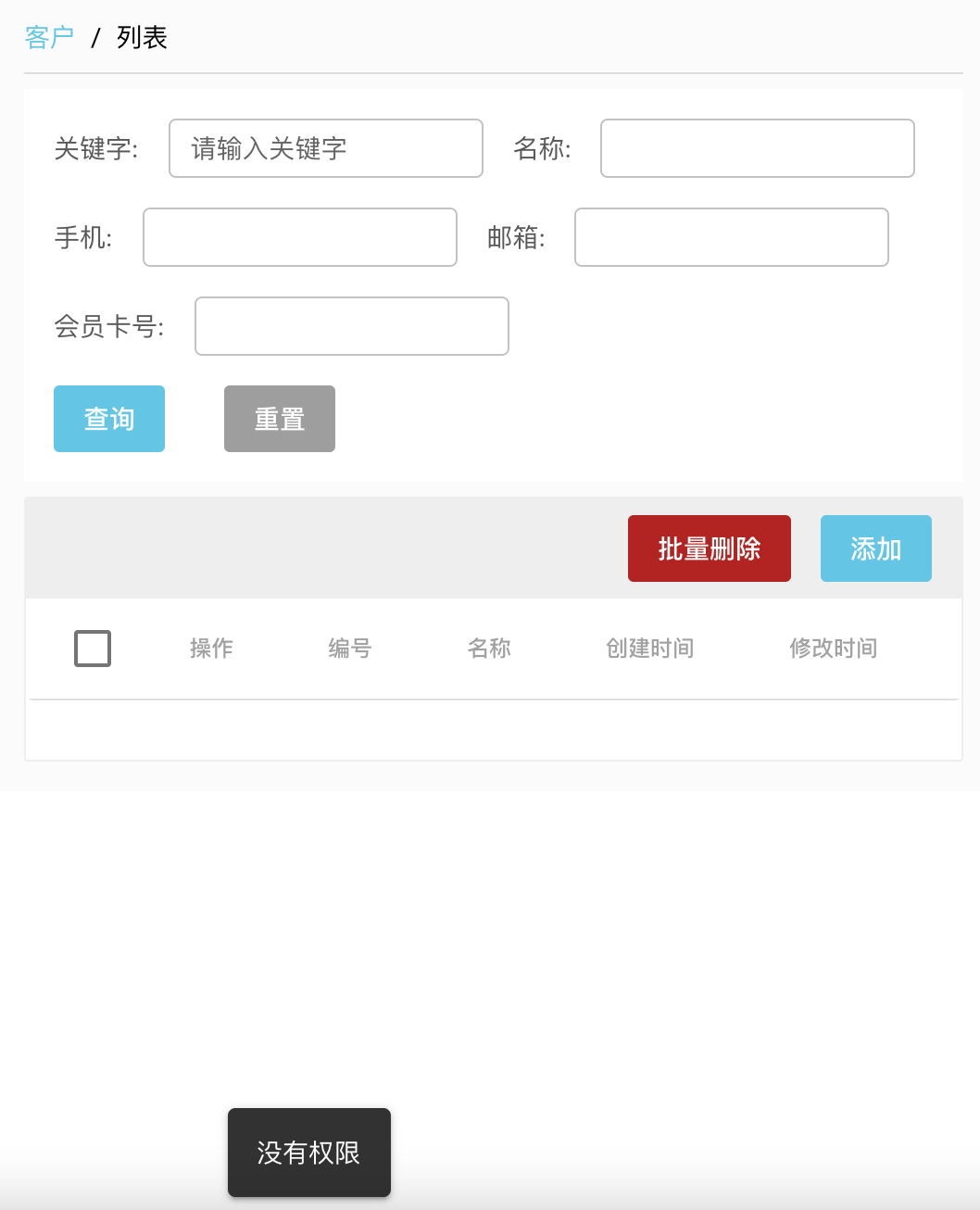 通过UI访问客户时候提示没有权限,和期望的效果一致
通过UI访问客户时候提示没有权限,和期望的效果一致
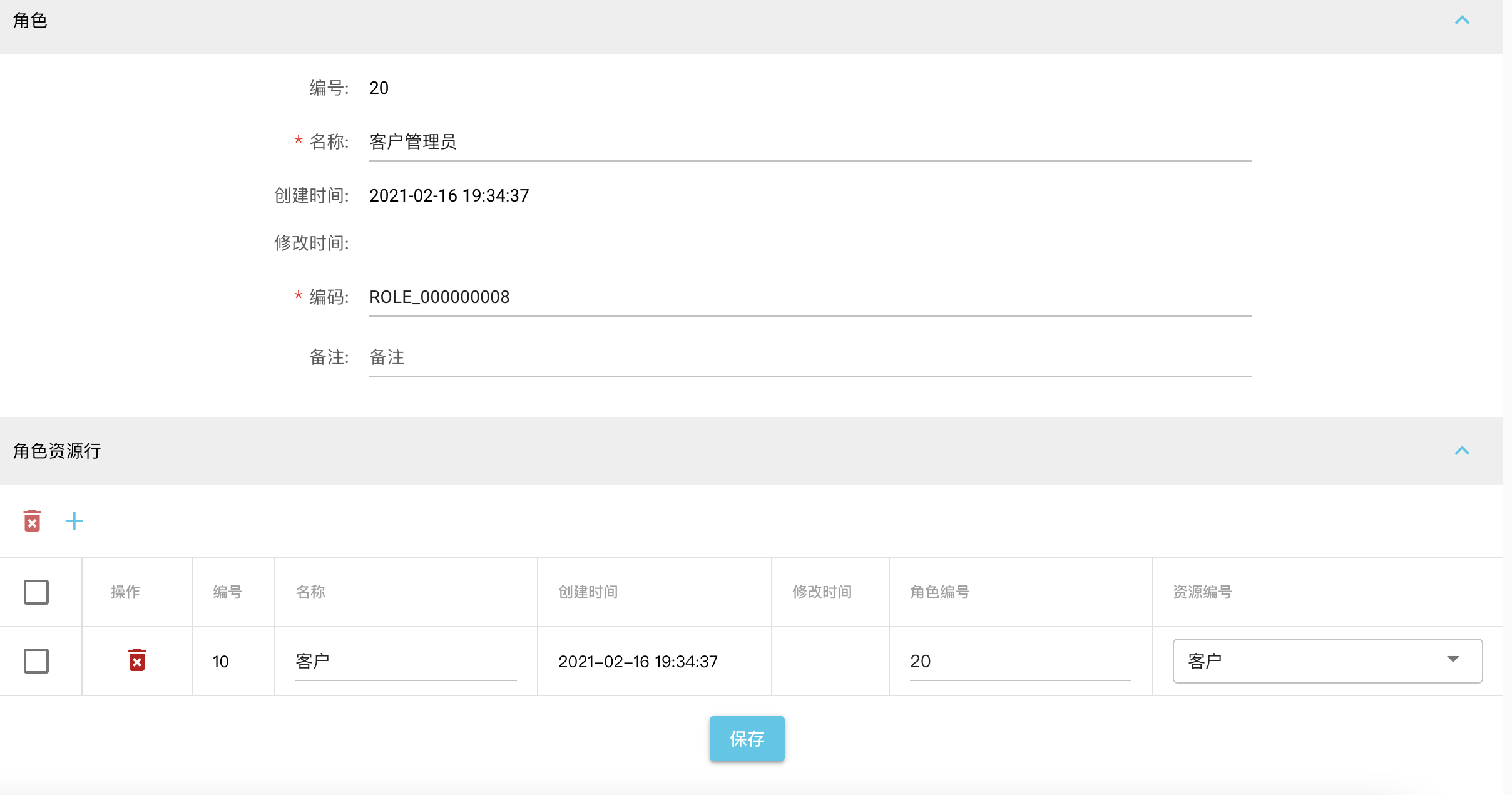 添加角色“客户管理员”,该角色拥有客户访问权限
添加角色“客户管理员”,该角色拥有客户访问权限
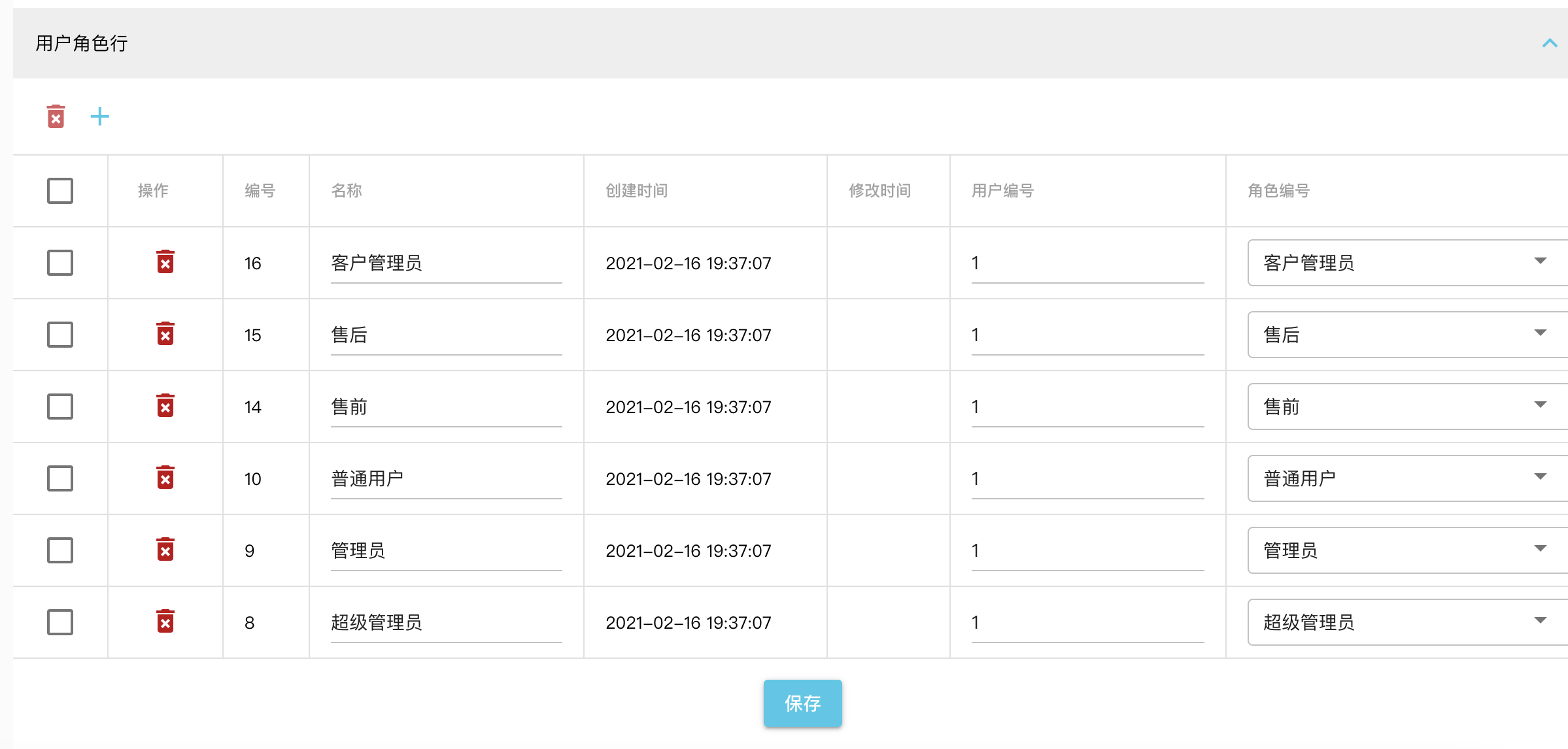 给“超级管理员”添加“客户管理员”角色,这样“超级管理员”就拥有了客户访问权限
给“超级管理员”添加“客户管理员”角色,这样“超级管理员”就拥有了客户访问权限
 因为用户重新分配了角色,需要需要注销重新登录,登录之后又可以正常访问客户资源了。
因为用户重新分配了角色,需要需要注销重新登录,登录之后又可以正常访问客户资源了。
# 核心源码
@Slf4j
@Component
public class DynamicSecurityMetadataSource implements FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource {
private static Map<String, ConfigAttribute> configAttributeMap = null;
@Autowired
private DynamicSecurityService dynamicSecurityService;
@PostConstruct
public void loadDataSource() {
configAttributeMap = dynamicSecurityService.loadDataSource();
}
public void clearDataSource() {
log.info("DynamicSecurityMetadataSource clearDataSource");
configAttributeMap.clear();
configAttributeMap = null;
}
@Override
public Collection<ConfigAttribute> getAttributes(Object o) throws IllegalArgumentException {
if (configAttributeMap == null) {
this.loadDataSource();
}
List<ConfigAttribute> configAttributes = new ArrayList<>();
FilterInvocation fi = (FilterInvocation) o;
String method = fi.getRequest().getMethod();
log.info("getAttributes method = " + method);
//获取当前访问的路径
String url = fi.getRequestUrl();
String path = URLUtil.getPath(url) + "_"+ method;
log.info("getAttributes url = " + url);
log.info("getAttributes path = " + path);
PathMatcher pathMatcher = new AntPathMatcher();
Iterator<String> iterator = configAttributeMap.keySet().iterator();
//获取访问该路径所需资源
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
String pattern = iterator.next();
if (pathMatcher.match(pattern, path)) {
log.info("match success = " + pattern + ", " + path);
configAttributes.add(configAttributeMap.get(pattern));
}
}
// 未设置操作请求权限,返回空集合
return configAttributes;
}
@Override
public Collection<ConfigAttribute> getAllConfigAttributes() {
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> aClass) {
return true;
}
}
继承FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource,实现getAttributes接口,通过http url加http method进行匹配
@Slf4j
@Component
public class DynamicAccessDecisionManager implements AccessDecisionManager {
@Override
public void decide(Authentication authentication, Object object,
Collection<ConfigAttribute> configAttributes) throws AccessDeniedException, InsufficientAuthenticationException {
// 当接口未被配置资源时直接放行
if (CollUtil.isEmpty(configAttributes)) {
log.info("empty configAttributes decide passed!");
return;
}
FilterInvocation fi = (FilterInvocation) object;
String method = fi.getRequest().getMethod();
log.info("decide method = " + method);
List<String> needAuthorityList = new ArrayList<String>();
Iterator<ConfigAttribute> iterator = configAttributes.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
ConfigAttribute configAttribute = iterator.next();
//将访问所需资源或用户拥有资源进行比对
String needAuthority = configAttribute.getAttribute();
needAuthorityList.add(needAuthority);
for (GrantedAuthority grantedAuthority : authentication.getAuthorities()) {
if (needAuthority.trim().equals(grantedAuthority.getAuthority())) {
return;
}
}
}
throw new AccessDeniedException("对不起,您没有资源:" + String.join(",", needAuthorityList) +"的访问权限!");
}
@Override
public boolean supports(ConfigAttribute configAttribute) {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> aClass) {
return true;
}
}
继承AccessDecisionManager,实现decide接口,将访问所需资源或用户拥有资源进行比对,如果拥有权限则放行,否则提示无权限。
# 小结
本文介绍了RBAC在crudapi中的实现原理,首先引入Spring security框架,然后利用配置生成用户,角色,资源等表单,通过配置实现基本的CRUD功能,最终实现了动态权限精细化管理。因为用户,角色等表与业务无关,所以会作为系统内置表单。
# 附demo演示
本系统属于产品级的零代码平台,不同于自动代码生成器,不需要生成Controller、Service、Repository、Entity等业务代码,程序运行起来就可以使用,真正0代码,可以覆盖基本的和业务无关的CRUD RESTful API。
官网地址:https://crudapi.cn (opens new window)
测试地址:https://demo.crudapi.cn/crudapi/login (opens new window)
